Difference Between Spotting and Period | Causes, Symptoms & Timing

Many menstruating women observe bleeding at various points during the month and often question whether it is spotting or a normal period. Although they both involve vaginal bleeding, they are not the same and typically indicate distinct internal reasons.
If you are aware of the difference between spotting and a menstrual period, it helps you to better monitor your cycle, notice potential health issues early and determine when to consult a doctor.
Menstrual health can feel confusing because bleeding patterns vary from person to person. Stress, hormones, age, contraception and lifestyle all influence how and when bleeding occurs. Some bleeding is completely normal, while other types may signal underlying issues that need attention.
This article explains the difference between spotting and periods, explores common causes, highlights when treatment is needed and shares practical guidance for managing both. The aim is to help you feel informed and confident about what your body is telling you.
What Is a Menstrual Period?
A menstrual period is the regular monthly shedding of the uterine lining when pregnancy does not occur. It is part of the menstrual cycle and usually starts during adolescence and continues until menopause.
A typical period lasts between three and seven days. The flow often starts light, becomes heavier for a few days and then tapers off. Menstrual blood is usually bright red to dark red and may include small clots. Cramping, back pain, bloating, breast tenderness and mood changes commonly accompany periods.
Periods occur at fairly predictable intervals, usually every 21 to 35 days. A consistent pattern often means the reproductive system functions normally. Changes in flow, timing or symptoms can happen occasionally and are not always a cause for concern.
What Is Spotting?
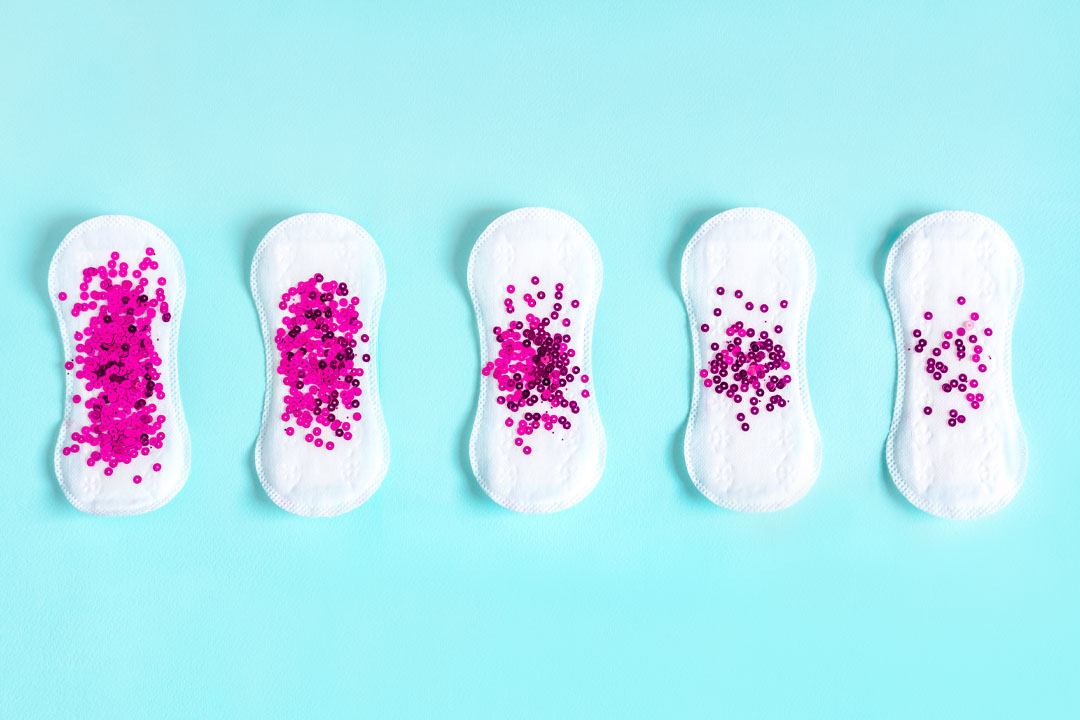
Spotting refers to light vaginal bleeding that happens outside your regular menstrual period. It usually involves a few drops of blood or light staining that does not require a pad or tampon.
The blood seen during spotting is often pink, brown or light red. Spotting does not follow the heavy flow pattern of a period and may last a few hours or a couple of days. Many people notice it only when wiping or as light marks on underwear.
Spotting can occur for many reasons. Some causes are harmless, while others may need medical attention. The timing, color and frequency of spotting often provide clues about why it is happening.
Key Differences Between Spotting and Period
Let us look at how spotting differs from a period and becomes easier when you look at specific features.
- Amount of bleeding: A period involves moderate to heavy bleeding that needs sanitary products. Spotting is very light and may not require protection.
- Timing: Periods follow a monthly cycle. Spotting occurs between periods or at unexpected times.
- Color of blood: Period blood is usually bright red or dark red. Spotting often appears pink, brown or rust colored.
- Duration: Periods last several days. Spotting usually lasts for a shorter time.
- Associated symptoms: Periods often come with cramps and fatigue. Spotting may occur without pain or discomfort.
Why Does Spotting Occur?
Spotting happens when something affects the delicate balance of hormones or the lining of the uterus. In many cases, it is temporary and resolves on its own.
- Hormonal fluctuations: Changes in estrogen and progesterone levels often cause spotting. This commonly happens during puberty, perimenopause or when starting or stopping hormonal birth control.
- Ovulation: Some people experience light spotting around ovulation, which occurs midway through the cycle. This is usually harmless and short lived.
- Birth control methods: Hormonal contraceptives such as pills, injections or intrauterine devices may cause spotting, especially in the first few months of use.
- Stress and lifestyle factors: Physical or emotional stress, sudden weight changes and intense exercise can disrupt hormonal balance and lead to spotting.
- Implantation bleeding: Light spotting may occur when a fertilized egg attaches to the uterine lining early in pregnancy. This usually happens around the time a period is expected.
When Is Spotting a Cause for Concern?
Spotting is not always harmless. Certain patterns suggest the need for medical evaluation. Frequent spotting between periods, bleeding after sex or spotting accompanied by pain may indicate an underlying issue. Infections, cervical changes, fibroids or hormonal disorders can all cause abnormal bleeding.
Postmenopausal spotting should always be checked since it is not considered normal after periods have stopped.
If spotting occurs during pregnancy, medical advice is important even if the bleeding seems light.
How to Track Spotting and Periods Effectively
Tracking your menstrual cycle helps identify patterns and detect changes early. Note the start and end dates of bleeding, the flow intensity and the color of blood. Record symptoms such as pain, fatigue or mood changes. Many people find cycle tracking apps helpful, but a simple calendar works well too.
Tracking becomes especially useful if you experience frequent spotting or irregular periods. This information helps healthcare providers understand what might be happening and suggest appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options for Spotting
Treatment for spotting depends on the cause, for instance:
- Hormonal regulation: If hormones cause spotting, doctors may adjust birth control methods or prescribe medication to stabilize hormone levels.
- Lifestyle changes: Managing stress, maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding extreme exercise can reduce hormone related spotting.
- Treating infections: Antibiotics or antifungal medicines treat infections that cause spotting.
- Monitoring only: If spotting is occasional and harmless, no treatment may be needed. Observation and tracking are often enough.
Spotting vs Period During Pregnancy
Bleeding during pregnancy causes anxiety, but not all bleeding signals a problem. Light spotting early in pregnancy can occur due to implantation or cervical sensitivity. However, bleeding with pain, dizziness or heavy flow requires immediate medical attention.
It is important not to assume bleeding during pregnancy is normal. Any bleeding should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
When Should You See a Doctor?
Medical advice is recommended if spotting happens often, periods become very heavy or bleeding occurs after menopause. Severe pain, fever or foul smelling discharge also need evaluation.
Trust your instincts. If something feels unusual or worrying, it is better to seek guidance than ignore symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can stress cause spotting between periods?
Yes, stress can disrupt hormone balance and lead to light bleeding between periods. Managing stress often helps restore normal menstrual patterns.
Is spotting normal when starting birth control?
Spotting is common during the first few months of hormonal birth control. It usually settles as the body adjusts to new hormone levels.
How long should a normal period last?
A typical period lasts three to seven days. Shorter or longer durations may still be normal if the pattern remains consistent.
Is brown blood spotting normal?
Brown spotting often represents old blood leaving the body. It is usually harmless, especially at the beginning or end of a cycle.
Can spotting mean pregnancy?
Spotting can occur in early pregnancy due to implantation. A pregnancy test and medical advice help confirm the cause.
Does spotting always mean a health problem?
No, occasional spotting can be normal. Persistent or painful spotting should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Can hormonal imbalance affect periods?
Yes, hormone imbalance can cause irregular periods, heavy bleeding or spotting. Treatment focuses on restoring hormonal balance.
Is spotting after sex normal?
Spotting after sex may result from cervical sensitivity or infection. Frequent episodes should be checked by a doctor.
Can heavy periods cause weakness?
Heavy periods can lead to iron deficiency and fatigue. Treatment may include iron supplements and cycle regulation.
When is spotting considered abnormal?
Spotting becomes abnormal when it is frequent, painful, occurs after menopause or is associated with other unusual symptoms.
Conclusion
Spotting and periods may look similar, but they serve different signals in menstrual health. Periods reflect the normal cycle, while spotting often points to hormonal changes or other temporary factors. Knowing the difference gives you the ability to identify when to go for treatment and what is typical for your body. A large number of menstruation issues can be safely and effectively controlled with appropriate tracking, early care and healthy practices.
About Us
AKsigen IVF is a premier center for advanced fertility treatments, with renowned fertility experts on our team. Specializing in IVF, ICSI, egg freezing, and other cutting-edge reproductive technologies, AKsigen IVF is committed to helping couples achieve their dream of parenthood. With personalized care and a patient-first approach, AKsigen IVF provides comprehensive fertility solutions under one roof.