Difference between IVF and ZIFT: Everything You Need to Know
When couples face infertility, they often explore assisted reproductive treatments. Two common options are in vitro fertilization (IVF) and zygote intrafallopian transfer (ZIFT).
Both procedures help achieve pregnancy by handling eggs and sperm outside the body. Yet, they differ in key steps, timing, and surgical needs. This guide will explain each method, highlight their similarities, and compare their pros and cons.
What Is In Vitro Fertilization (IVF)?
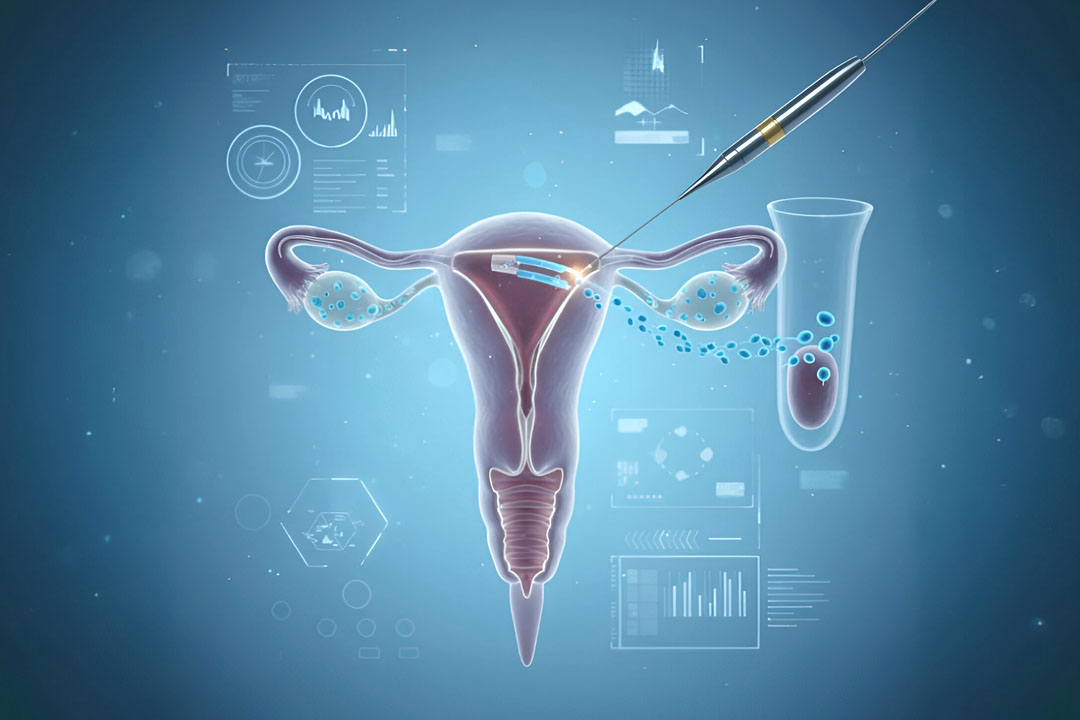
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a fertility treatment in which eggs and sperm join in a laboratory setting. “In vitro” means “in glass,” referring to the lab dishes where fertilization takes place.
Step-by-Step Process
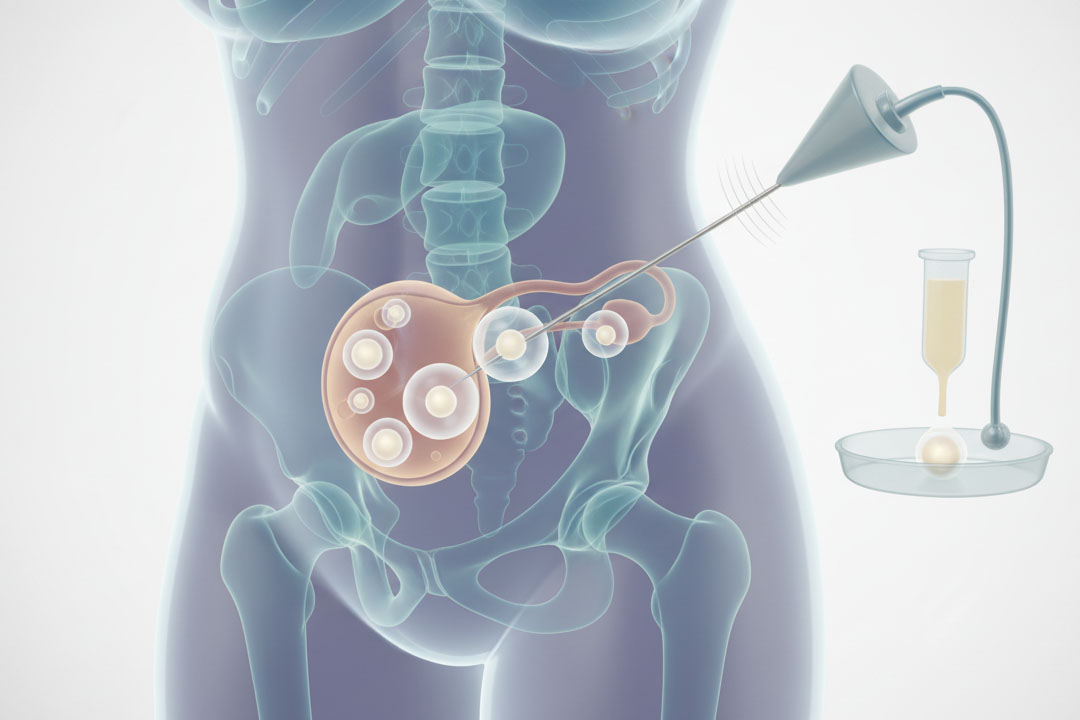
- Ovarian Stimulation: Doctors give hormone injections to encourage the ovaries to produce multiple eggs instead of the single egg released in a natural cycle.
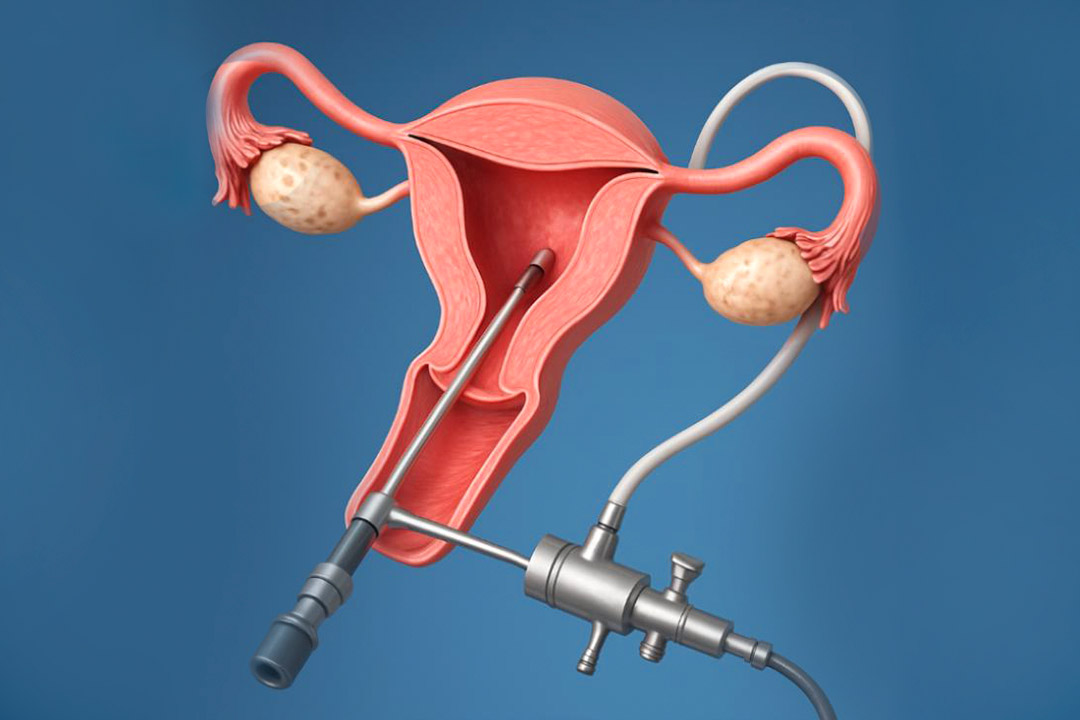
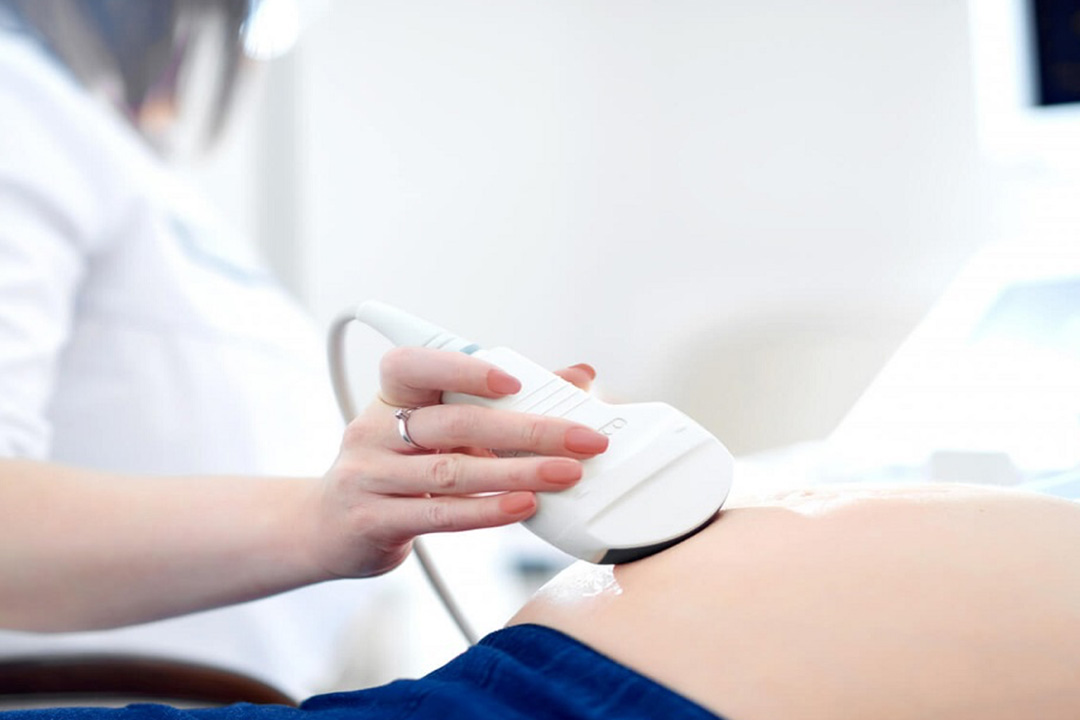
- Egg Retrieval: About 36 hours after the final hormone dose, the specialist uses a thin needle guided by ultrasound to collect the mature eggs from the ovaries. This minor procedure takes 15–30 minutes under light sedation.
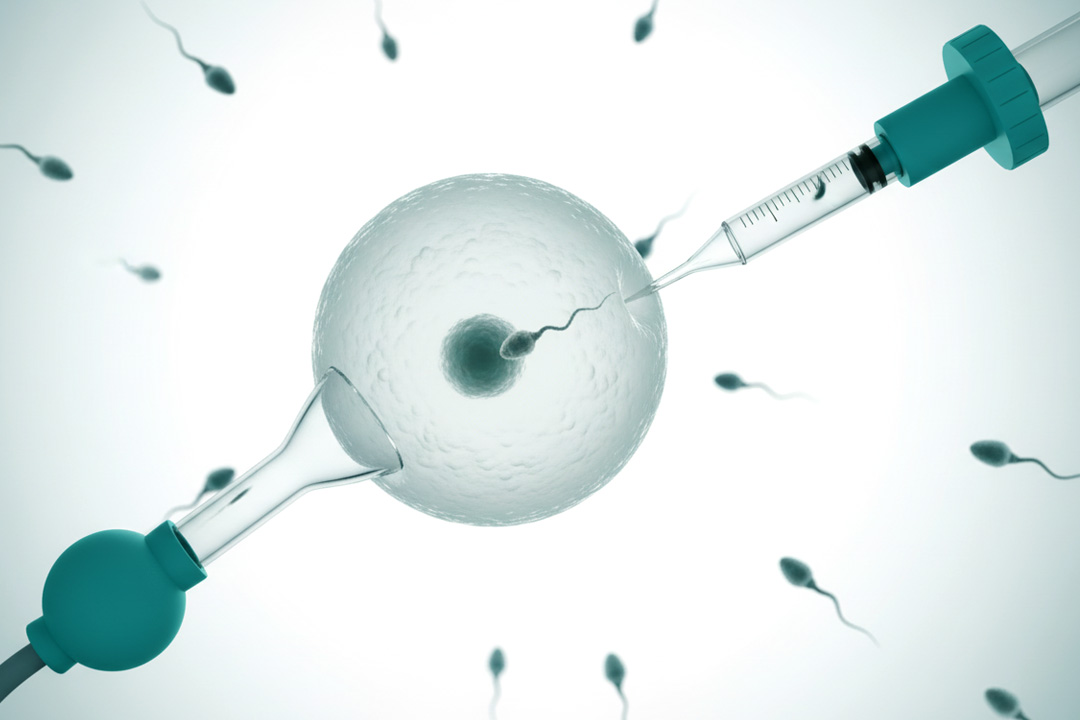
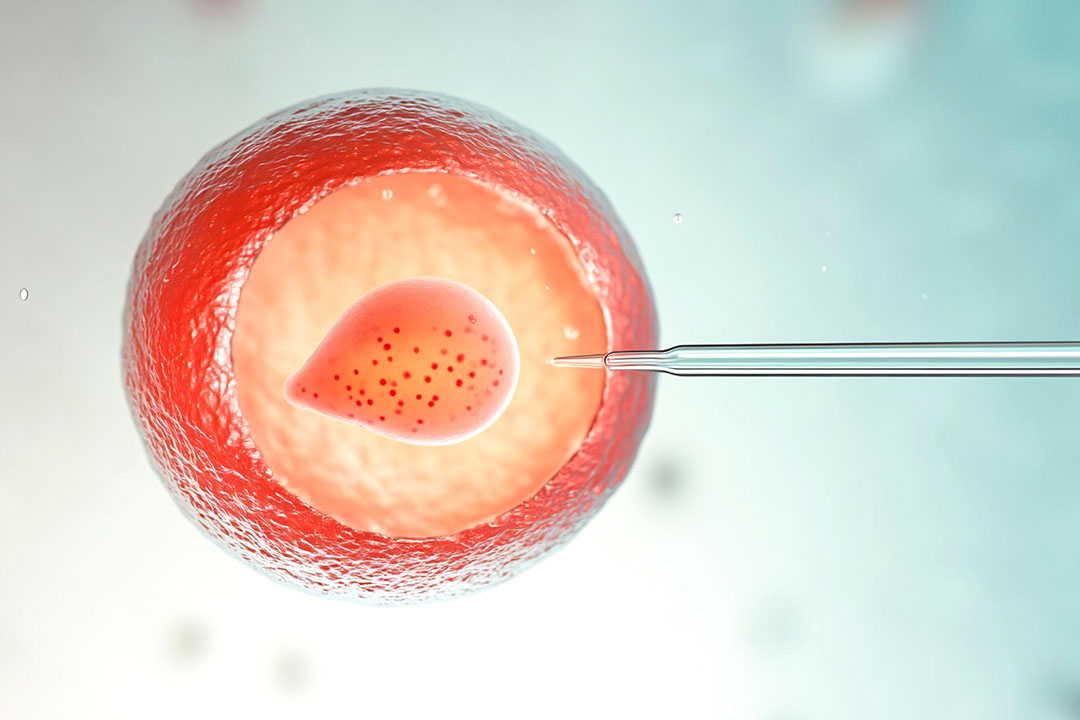
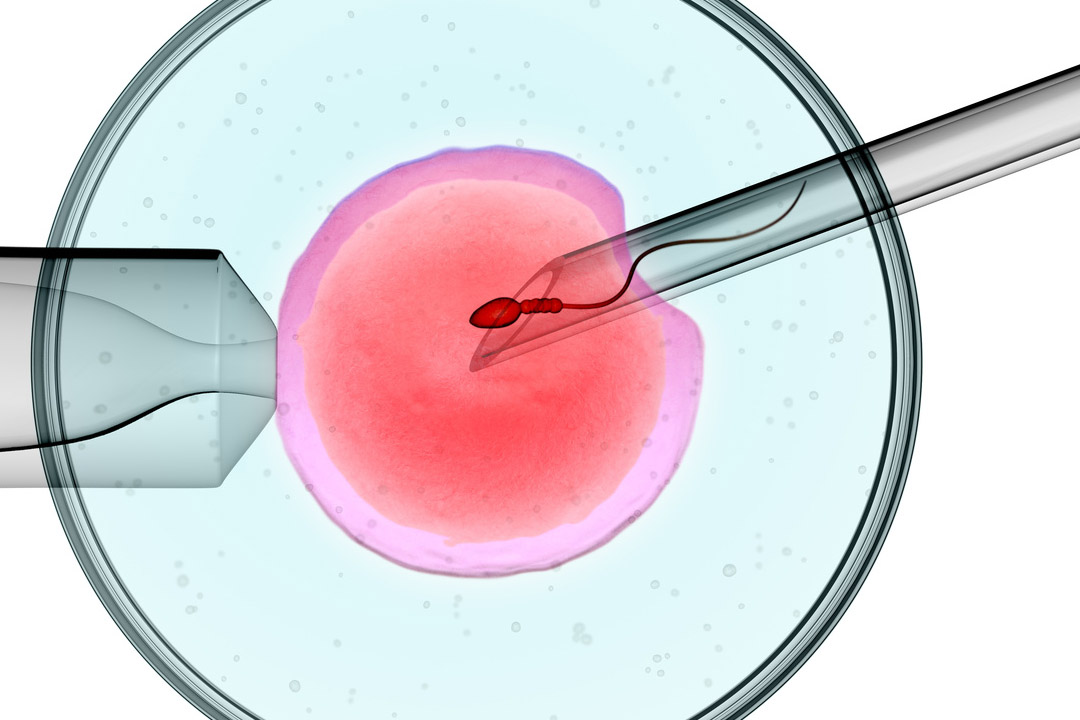
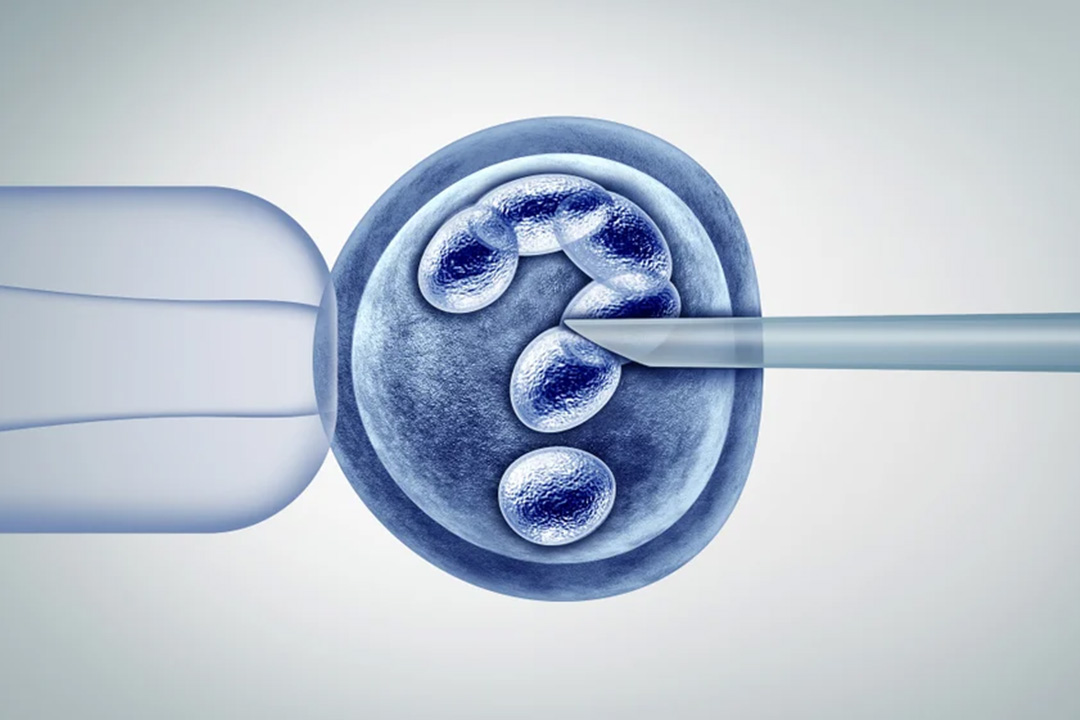
- Fertilization in the Lab: In the lab, technicians place healthy sperm and eggs together in culture dishes. In some cases, they inject a single sperm directly into an egg.
- Embryo Culture: Embryos grow in a controlled environment for 3 to 5 days. During this time, specialists monitor their development and select the healthiest ones.
- Embryo Transfer: A thin catheter transfers one or more embryos into the woman’s uterus. This step does not require surgery and causes little to no discomfort.
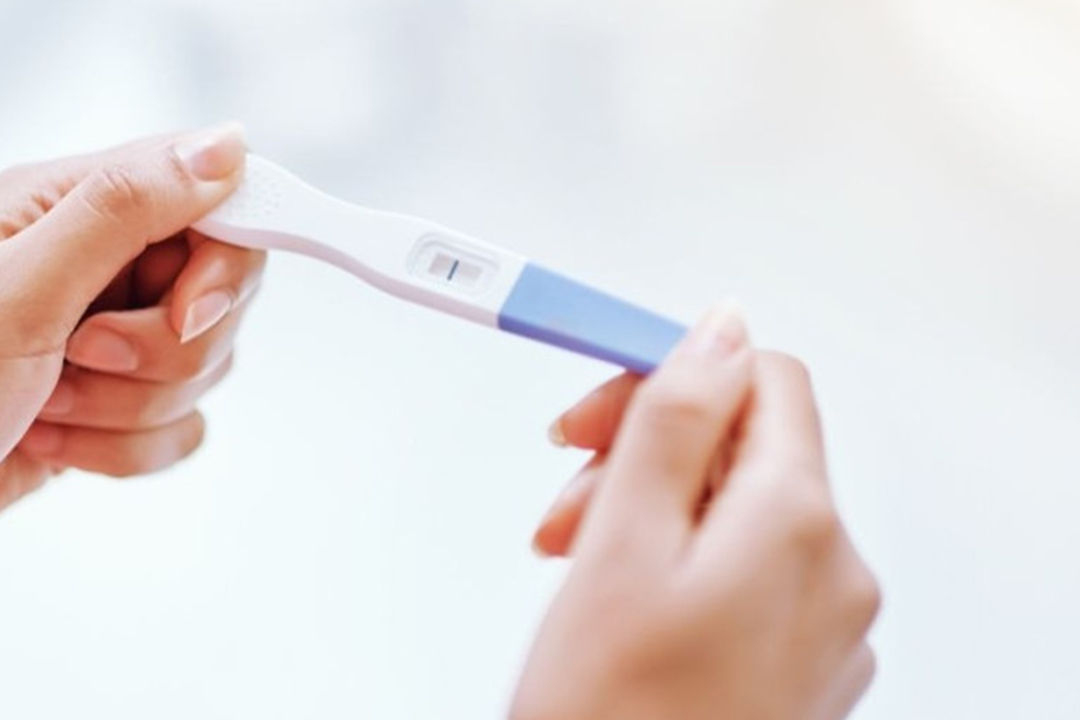
- Pregnancy Test: About two weeks later, a blood test checks for the pregnancy hormone (hCG) to confirm success.
Key Points
- Embryos grow for several days before transfer.
- No surgery is needed for the transfer step.
- IVF works even if fallopian tubes are blocked or damaged.
What Is Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer (ZIFT)?
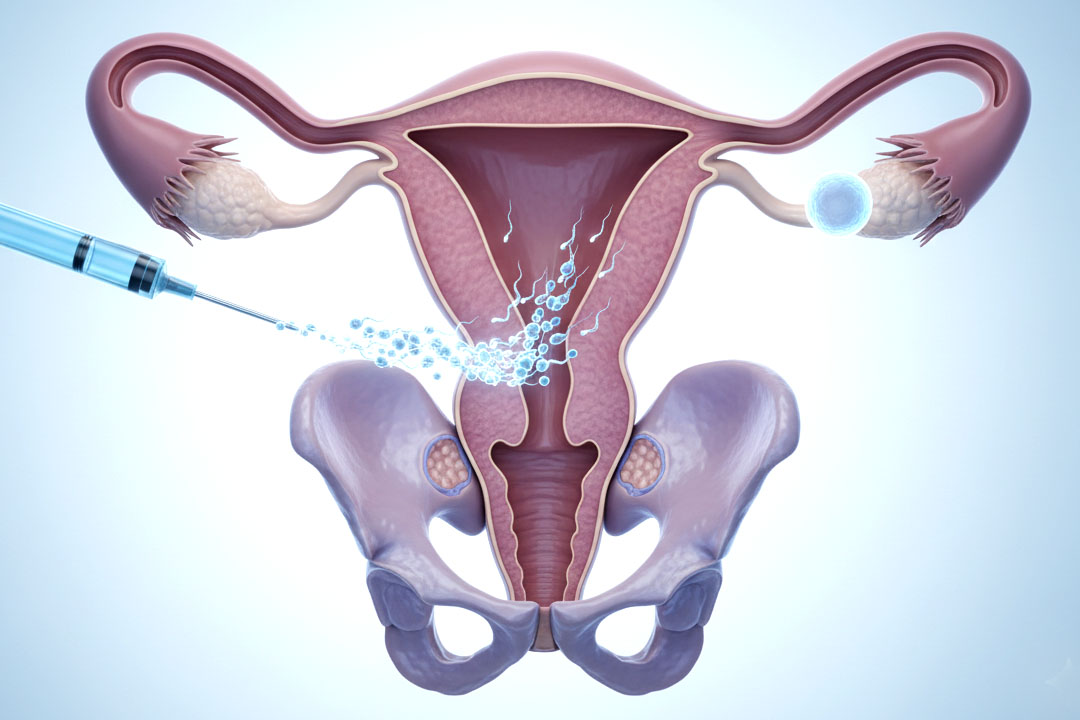
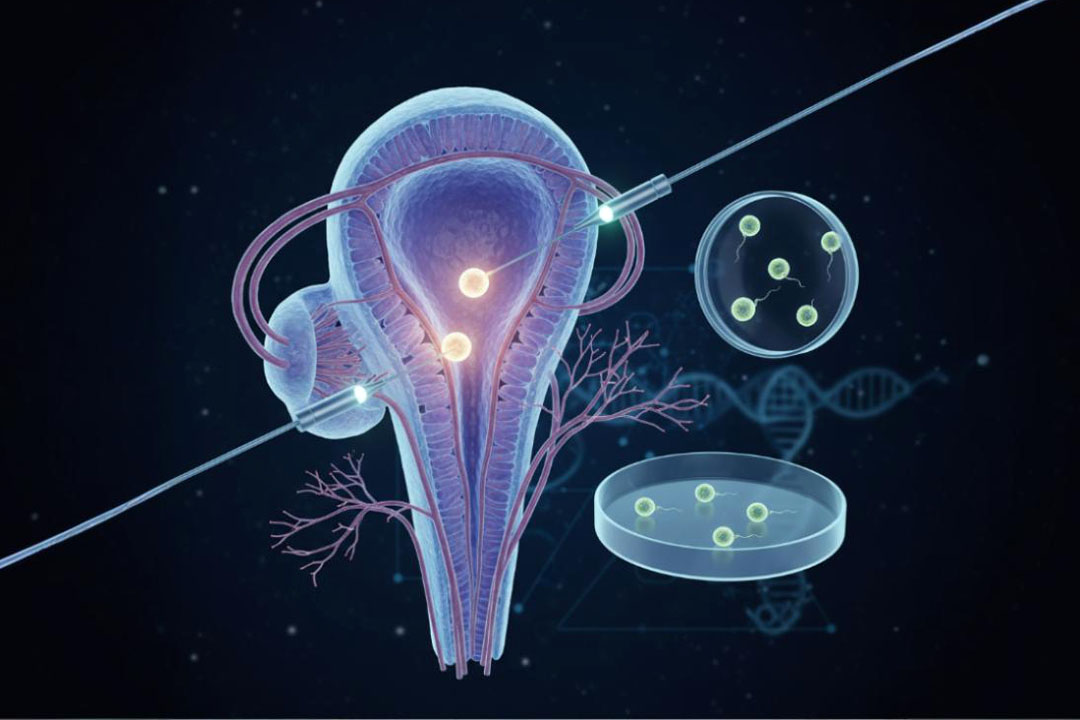
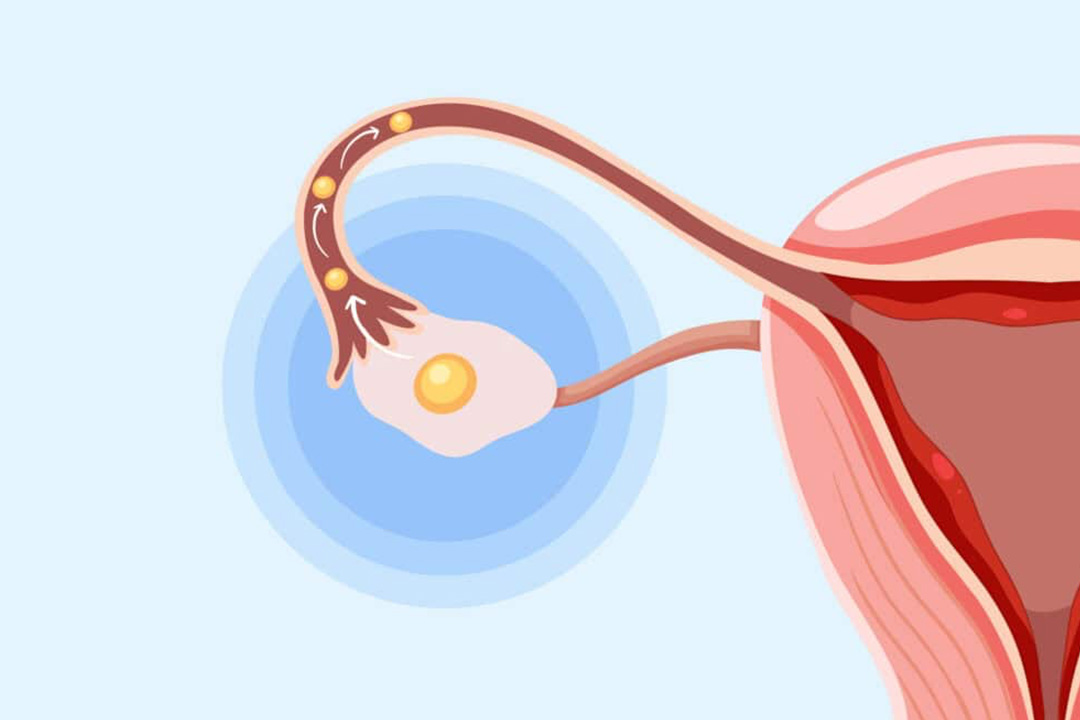
Zygote intrafallopian transfer (ZIFT) is an assisted reproductive procedure like IVF, with one main difference: the fertilized egg (zygote) enters the fallopian tube instead of the uterus. Because the embryo goes directly into the tube, ZIFT is also called tubal embryo transfer (TET).
Step-by-Step Process
- Ovarian Stimulation: As in IVF, women receive hormone injections to produce several mature eggs.
- Egg Retrieval: A minor aspiration procedure collects the eggs under light sedation and ultrasound guidance.
- Fertilization in the Lab: Technicians fertilize the eggs with sperm in a dish. In ZIFT, fertilization happens outside the body but within 24 hours.
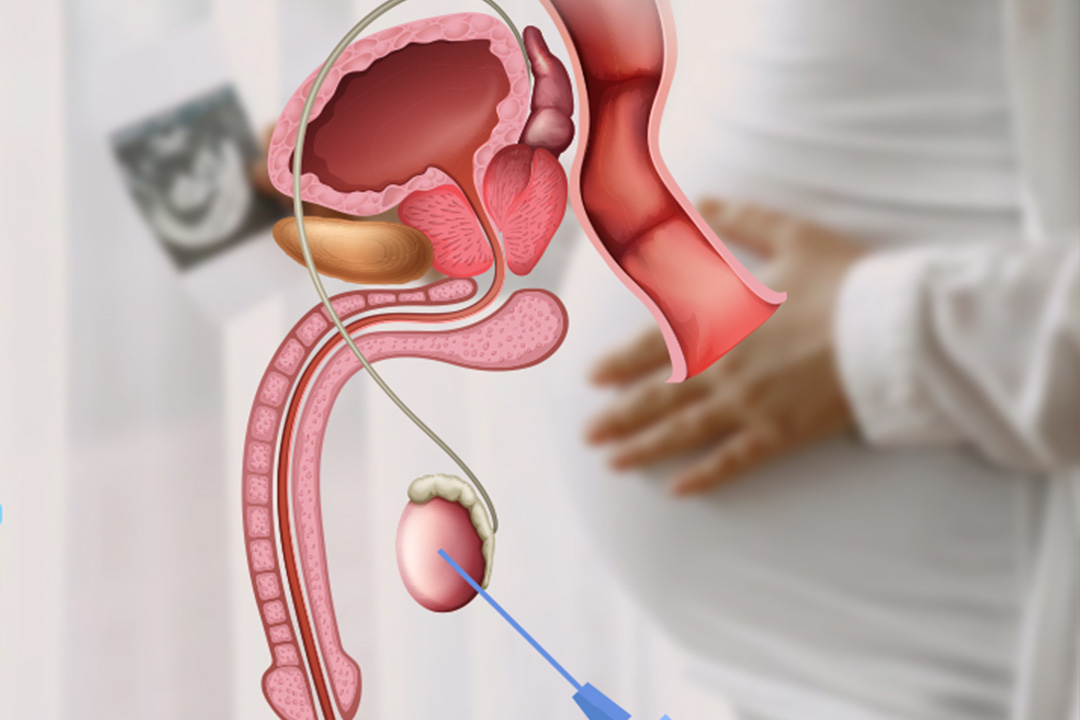
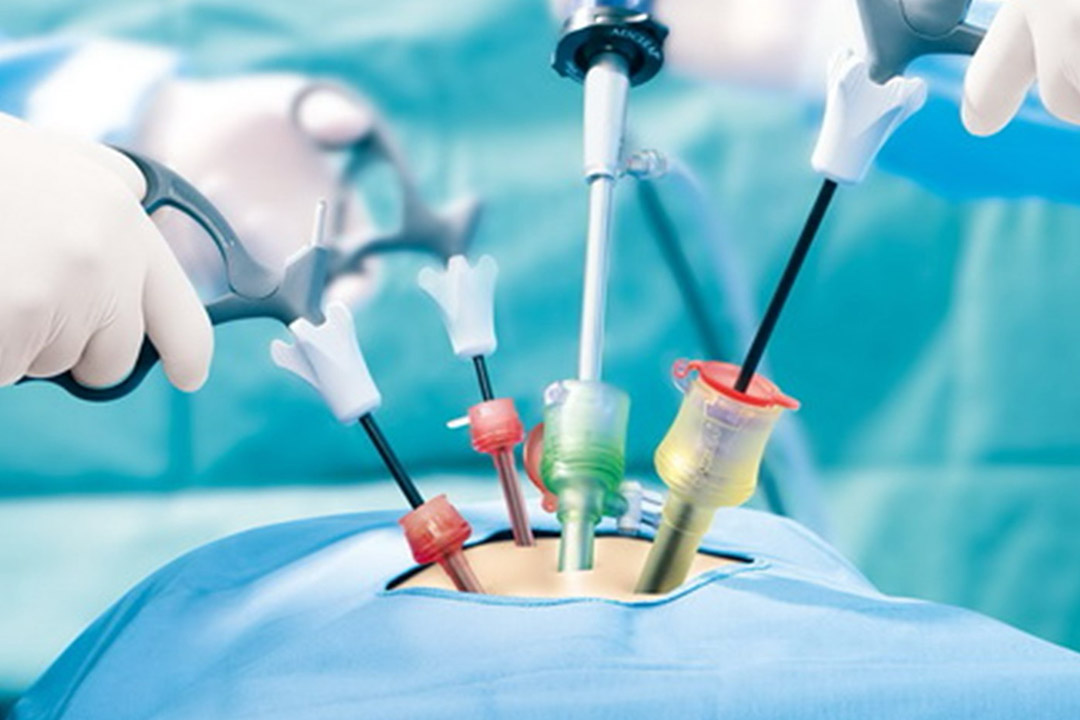
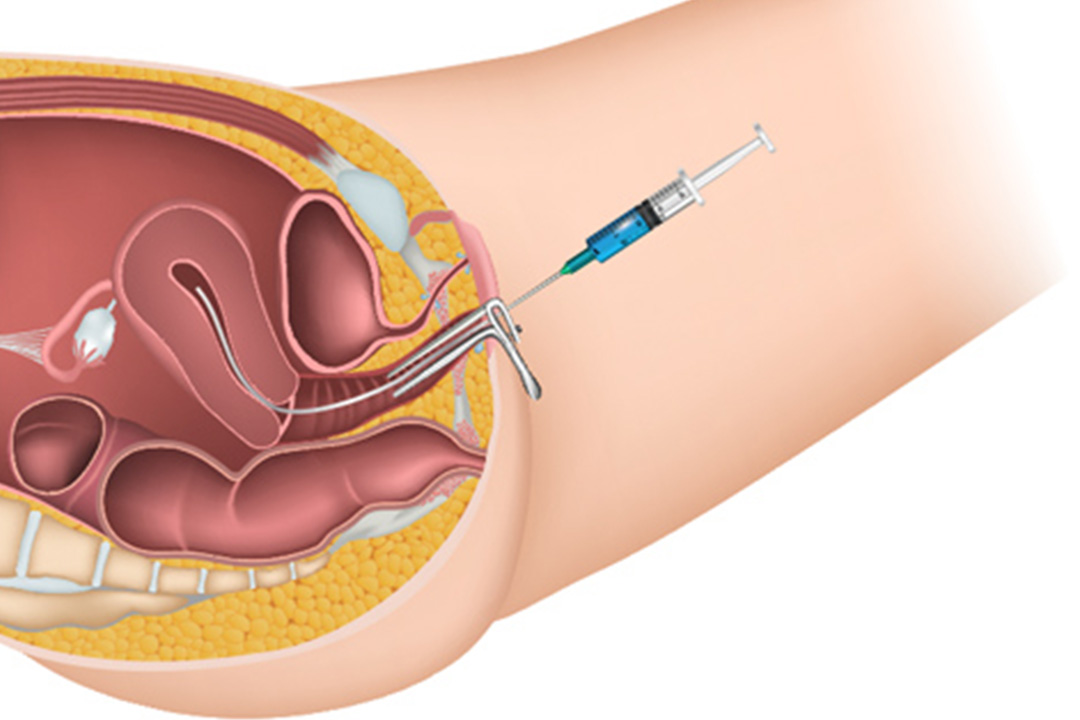
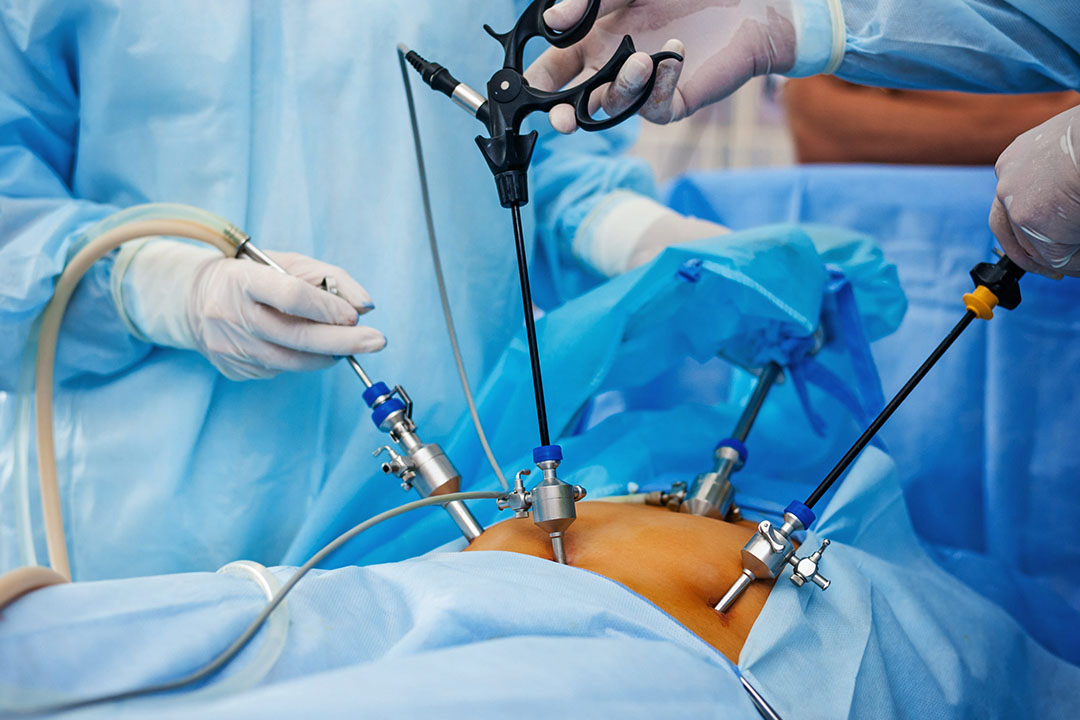
- Embryo Transfer into Fallopian Tube: A surgeon performs laparoscopy, making a small incision near the navel. Through this opening, a catheter places the fertilized eggs (zygotes) into the fallopian tube.
- Pregnancy Test: After about two weeks, a blood test confirms pregnancy.
Key Points
- Fertilized eggs transfer within 24 hours of fertilization.
- The transfer requires a surgical procedure (laparoscopy).
- A woman must have healthy fallopian tubes for ZIFT to work.
Similarities Between IVF and ZIFT
Ovarian Stimulation
Both treatments start by stimulating the ovaries with hormone injections to retrieve multiple eggs.
Egg Retrieval and Lab Fertilization
Specialists collect eggs using the same minor aspiration method. They then fertilize the eggs in the lab using standard IVF techniques.
Embryo Culture
Each method allows embryologists to observe early embryo development and choose the best-quality embryos for transfer.
Candidate Profile
Both methods suit couples with tubal damage, severe male factor infertility, or unexplained infertility. They offer hope when simpler treatments fail.
Key Differences Between IVF and ZIFT
| Parameter | IVF | ZIFT |
| Embryo Transfer Location | Uterus | Fallopian tube |
| Timing | 3–5 days after fertilization | Within 24 hours of fertilization |
| Surgical Need | No surgery for transfer (catheter via cervix) | Requires laparoscopy to access the fallopian tube |
| Tubal Health | Works even if tubes are blocked or damaged | Requires normal, healthy fallopian tubes |
| Fertilization | Must wait for embryo development to confirm success | Fertilization is confirmed in lab before transfer |
| Recovery | Minimal discomfort after transfer | Slightly longer recovery due to laparoscopy |
Who Is a Good Candidate for IVF?
- Blocked or Damaged Tubes: IVF bypasses fallopian tubes altogether, making it ideal when tubes cannot transport eggs or embryos.
- Male Factor Infertility: IVF with intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) helps when sperm count or motility is very low.
- Advanced Maternal Age: IVF allows selection and screening of embryos, aiding older women in achieving healthy pregnancy.
- Genetic Screening Needs: Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) checks embryos for genetic disorders before transfer.
Who Is a Good Candidate for ZIFT?
Not everyone can opt for ZIFT, it require some factors which are as follows:
- Since ZIFT places embryos in the tube, both tubes must be open and functioning.
- ZIFT confirms fertilization in the lab before transfer, offering certainty that the embryo formed.
- Couples who did not succeed with IVF or gamete intrafallopian transfer (GIFT) may try ZIFT as an alternative.
- Some couples may prefer ZIFT to mimic as closely as possible natural conception, with the embryo traveling naturally from tube to uterus.
Advantages and Disadvantages
IVF Advantages
- No Surgery for Transfer: Transfers occur through the cervix, avoiding surgical risks.
- Suitable for Tubal Issues: Success does not depend on tubal health.
- Advanced Genetic Testing: Embryos can undergo PGT, reducing the risk of genetic disorders.
IVF Disadvantages
- Embryo Implantation Uncertainty: You cannot confirm fertilization before transfer.
- Possible Multiple Births: Transferring more than one embryo may raise the chance of twins or higher-order multiples.
ZIFT Advantages
- Confirmed Fertilization: Doctors see a fertilized embryo before transfer, ensuring only viable zygotes enter the body.
- Natural Embryo Transport: Placement in the tube allows the embryo to move naturally to the uterus.
ZIFT Disadvantages
- Surgical Risks: Laparoscopy carries risks of anesthesia, bleeding, or infection.
- Requirement for Healthy Tubes: Not suitable if tubes are blocked, damaged, or scarred.
- Recovery Time: Patients may need more rest after surgery compared to IVF transfer.
Success Rates
Success rates for both IVF and ZIFT depend on factors like age, cause of infertility, and clinic expertise. In general:
- IVF Success: Younger women often see 40–50% success per cycle. Success decreases with age.
- ZIFT Success: Reports suggest similar or slightly higher success compared to IVF in well-selected patients with good tubal health. ZIFT may offer a pregnancy rate of 45–55% per cycle for women under 35.
Risks and Considerations
Both procedures involve hormone injections that can cause side effects such as mood swings, bloating, or ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). Other considerations include:
- Multiple Pregnancy Risk: Transferring multiple embryos raises the chance of twins or triplets.
- Procedure Costs: IVF and ZIFT may have different price points. ZIFT’s laparoscopy adds surgical fees.
- Insurance Coverage: Coverage varies by region and policy. Check with your provider to understand your benefits.
Cost Considerations
ZIFT (Zygote Intrafallopian Transfer) is a fertility treatment that involves placing a zygote (fertilized egg) into the fallopian tube. In India, a ZIFT cycle can cost between Rs. 75,000 to Rs. 2,50,000, but this is just an average, and the actual cost can vary.
This cost can be influenced by factors like the clinic chosen, the type of ZIFT procedure (e.g., natural ZIFT), and additional procedures or medications required.
Conclusion
IVF and ZIFT both offer a path to parenthood for couples facing infertility. In vitro fertilization allows fertilized embryos to develop in the lab for several days before placing them directly into the uterus. Zygote intrafallopian transfer, by contrast, moves fertilized eggs into the fallopian tube within a day of fertilization, letting embryos travel naturally to the uterus.
About Us
AKsigen IVF is a premier center for advanced fertility treatments, with renowned fertility experts on our team. Specializing in IVF, ICSI, egg freezing, and other cutting-edge reproductive technologies, AKsigen IVF is committed to helping couples achieve their dream of parenthood. With personalized care and a patient-first approach, AKsigen IVF provides comprehensive fertility solutions under one roof.