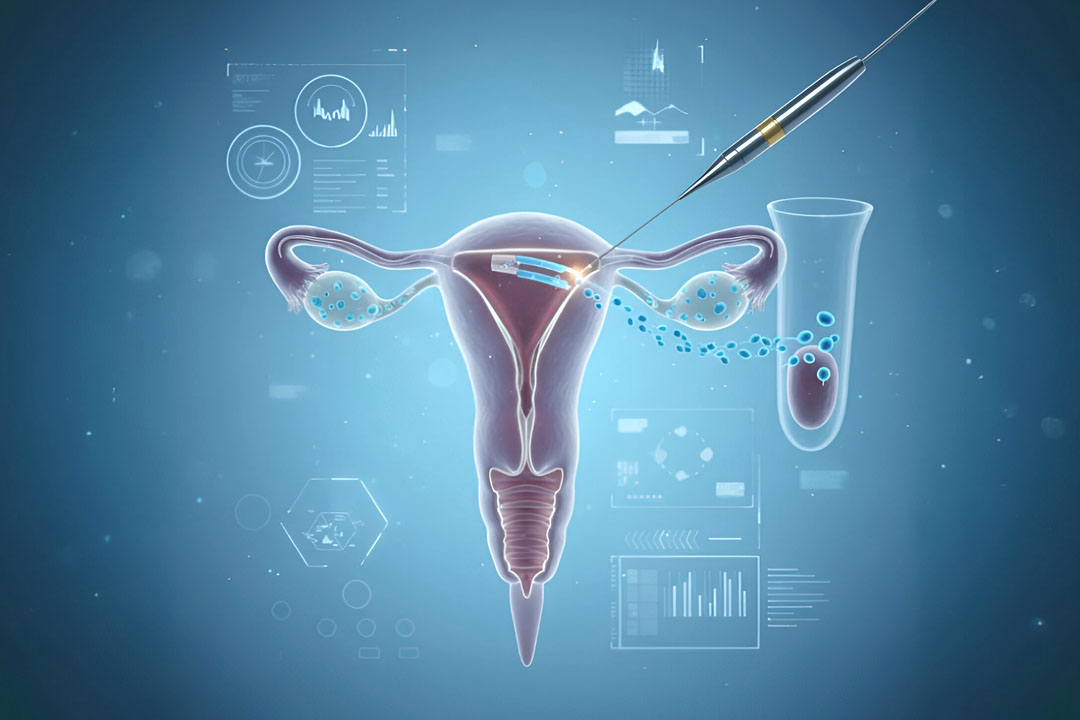
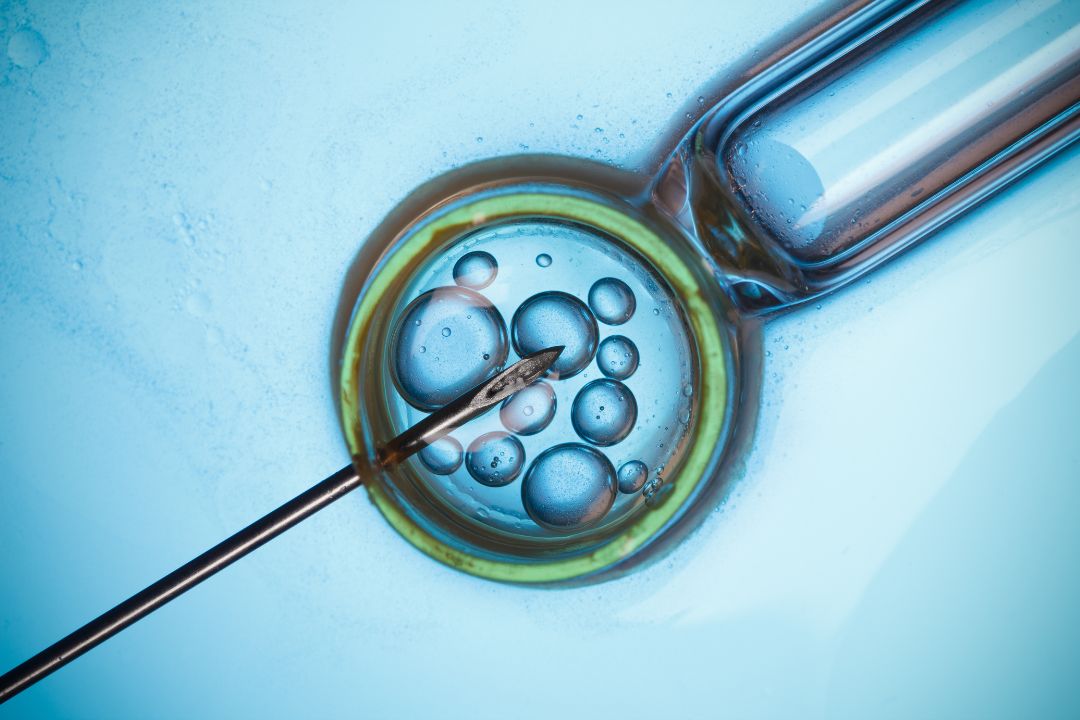
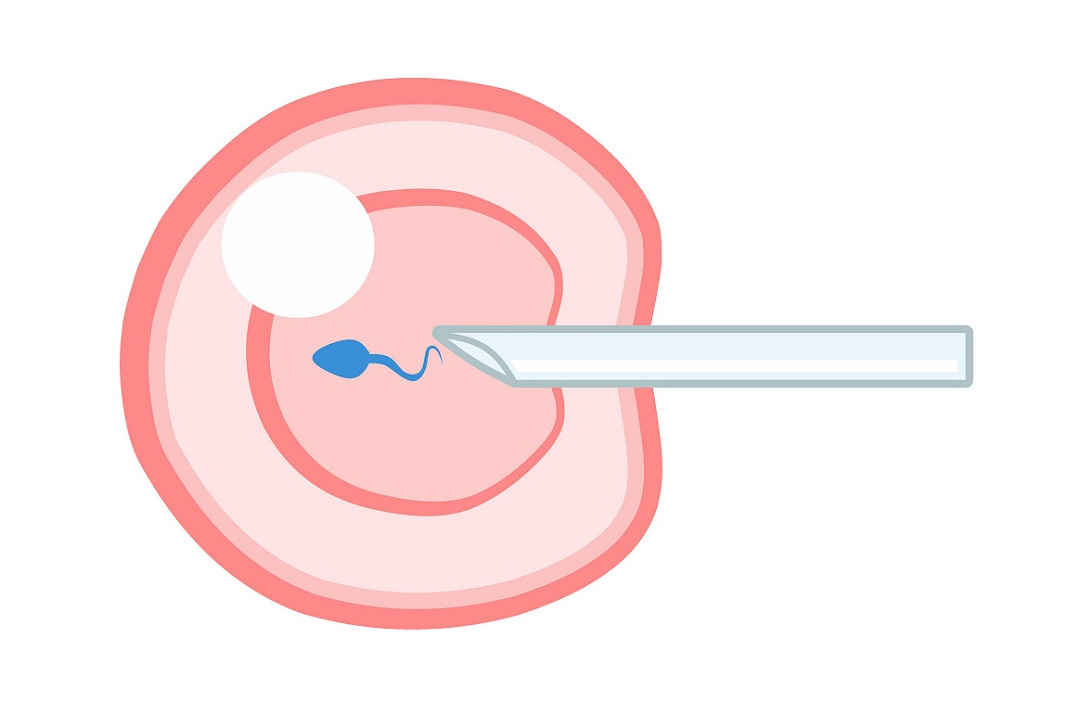
What is Laser Assisted Hatching in IVF?
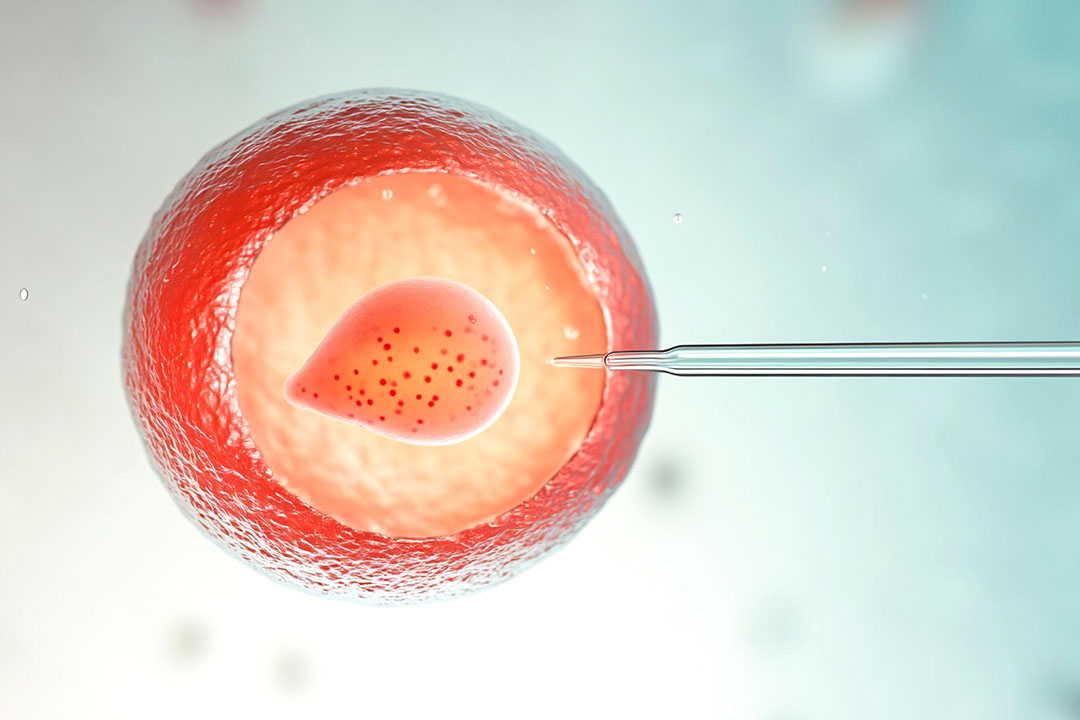
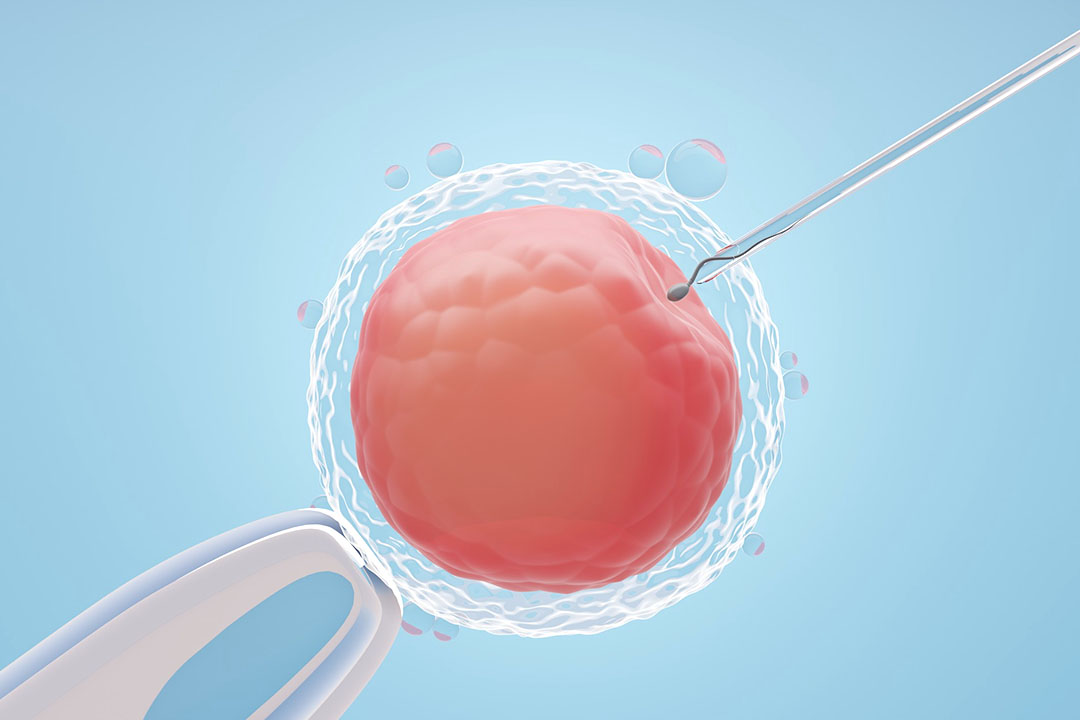
Laser assisted hatching (LAH) is an innovative technique used during in vitro fertilization (IVF) to help improve the chances that an embryo will successfully attach to the uterine wall.
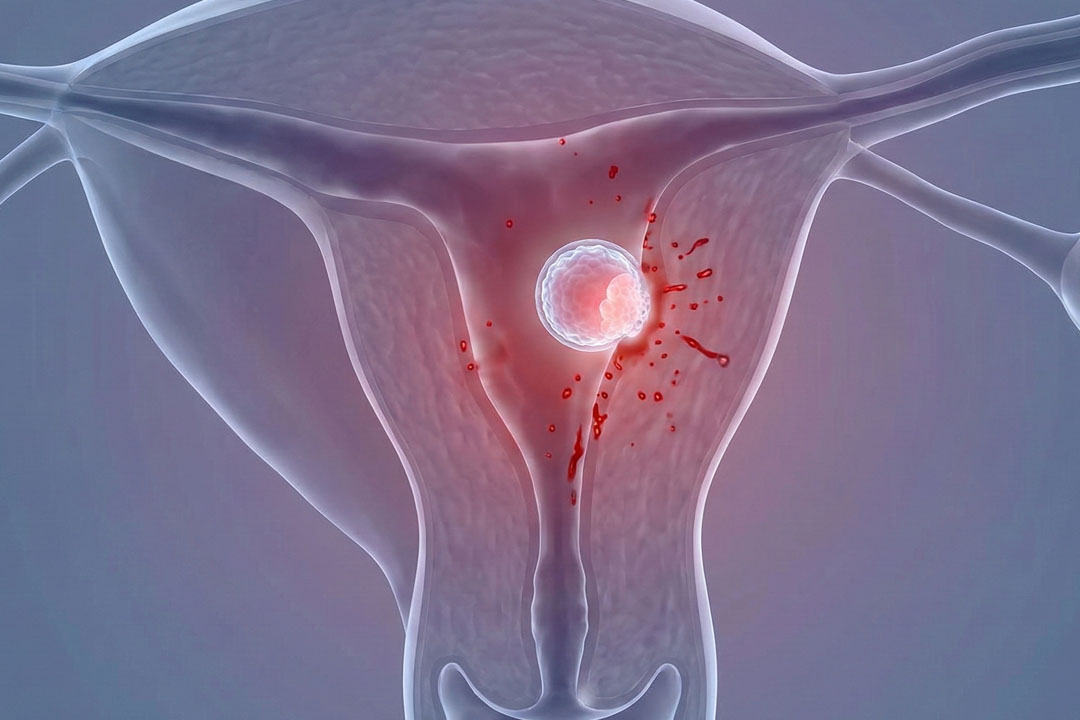
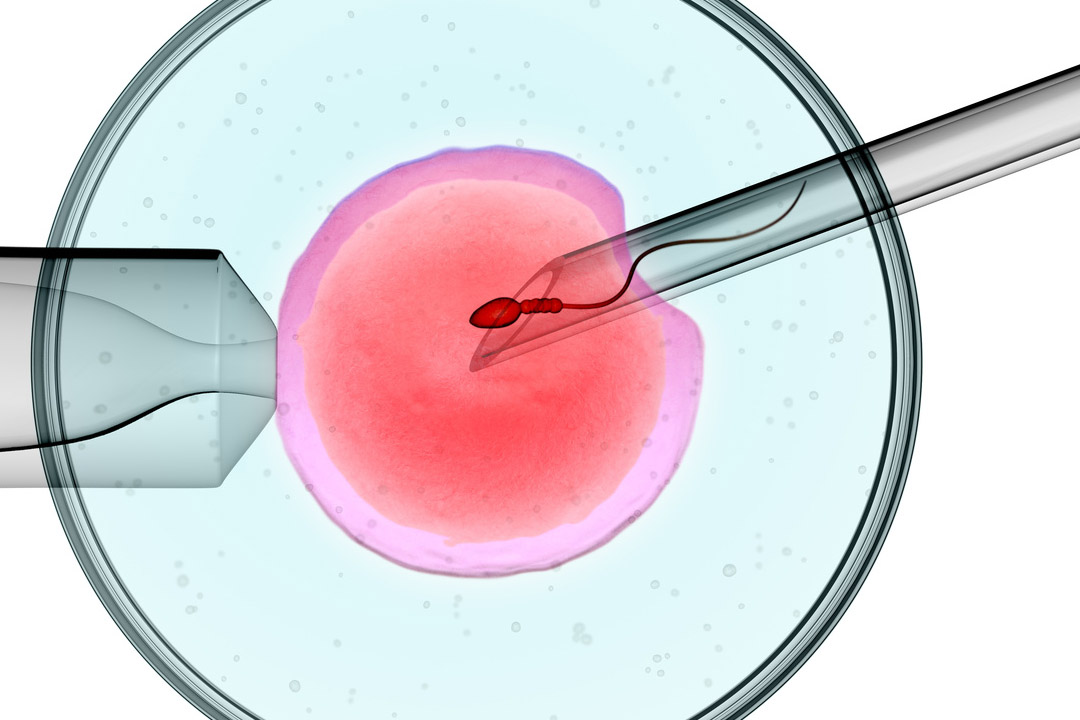
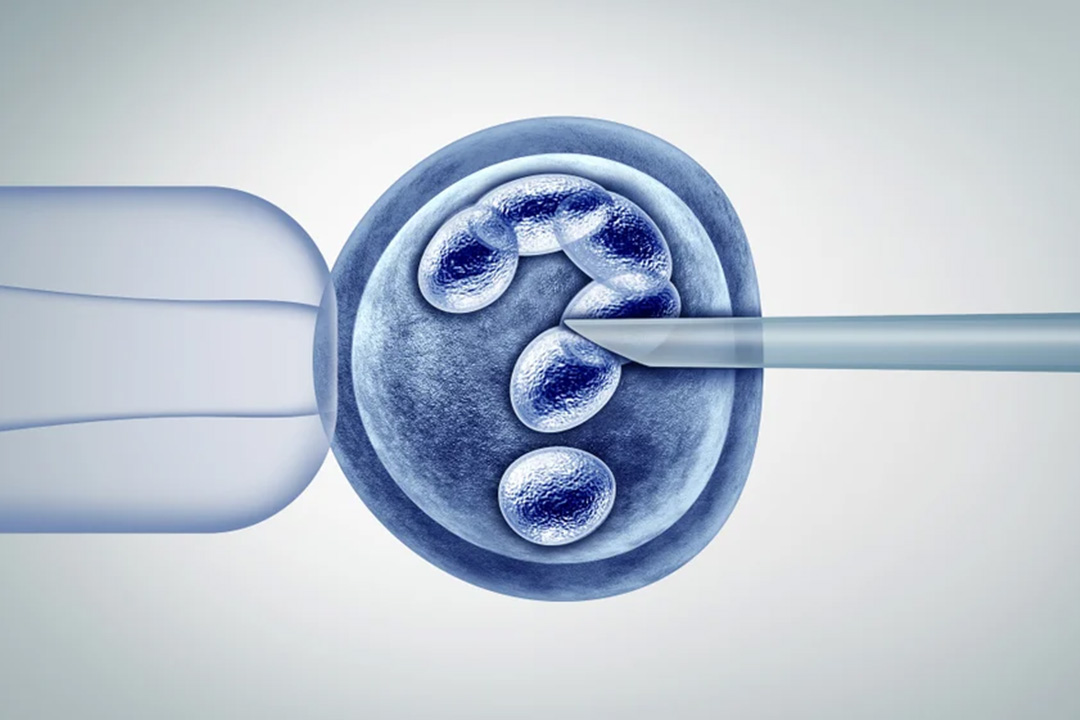
This procedure uses a highly focused laser to create a small opening or to thin the hard protective outer layer known as the zona pellucida that surrounds the embryo. The embryo is better able to “hatch” out of its shell, which is a critical step in allowing it to implant in the uterus and ultimately grow into a healthy pregnancy.
In this article, we’ll walk you through exactly what laser assisted hatching is, how the procedure works, and who might benefit from it. We’ll also look at its success rates and the risks you should be aware of.
The Role of the Zona Pellucida and the Natural Hatching Process
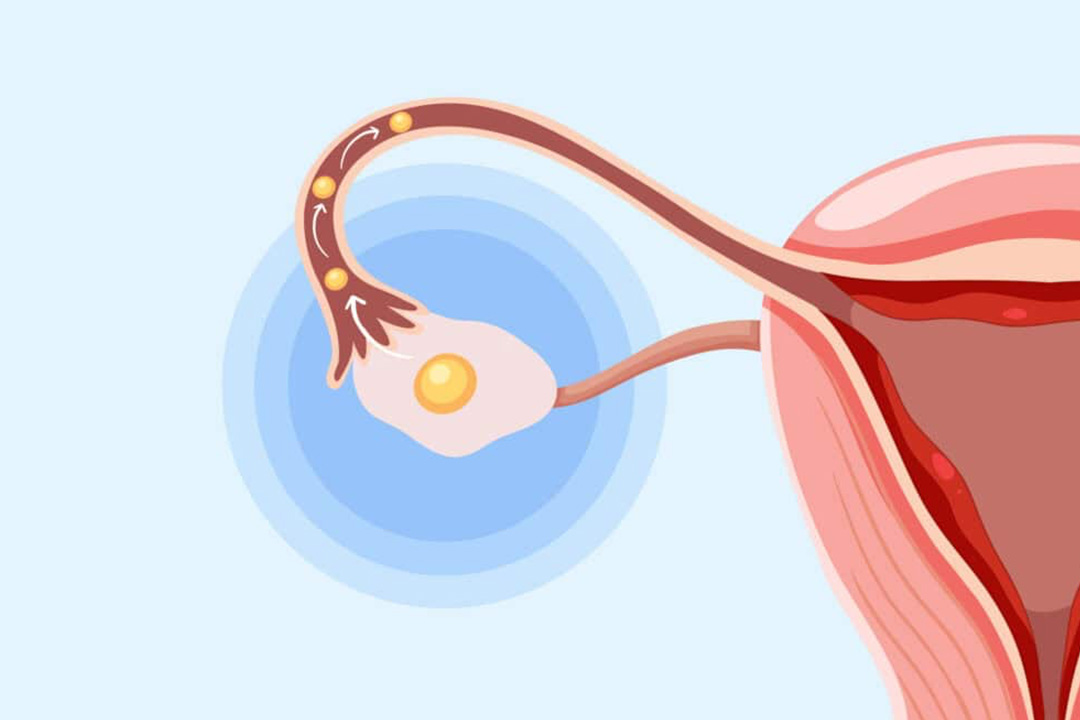
Before we dive into the specifics of laser assisted hatching, it helps to understand a little about how early embryonic development works. Every embryo that develops in the early stages of IVF is enclosed in a protective shell called the zona pellucida. For a successful pregnancy, though, this shell isn’t meant to be permanent.
During natural development, the embryo must break out of this shell in a process called “hatching” to allow it to attach to the uterine lining. Sometimes the zona pellucida can become unusually thick or hard.
This can happen naturally, or it might even occur after laboratory procedures like cryopreservation (the process of freezing embryos for later use). When this happens, the embryo might have a hard time breaking free on its own, which can reduce the chances for a successful implantation.
Laser assisted hatching comes into play by delicately weakening or opening the zona pellucida so that the embryo can hatch more easily. This seemingly small step can make a big difference in helping the embryo embed itself in the uterine wall where it can develop further.
What Exactly Is Laser Assisted Hatching (LAH)?
LAH is a technique where embryologists use a very precise laser to target the zona pellucida. Here’s what happens:
The embryologist uses a high-powered laser that emits extremely short pulses of light. This laser is aimed at a specific spot on the zona pellucida usually at the area farthest from the embryo’s inner cells to ensure that the inner cell mass is not harmed.
The outer shell is either thinned or a tiny opening is created with a few controlled laser pulses (often around three to five). This intervention helps the embryo to break out of its shell more easily when it’s time to hatch.
The procedure is carried out under strict laboratory conditions using state-of-the-art equipment, and it typically takes only a few seconds to perform. The goal of LAH is to assist embryos that might naturally struggle with hatching due to a tougher-than-average zona pellucida, thereby potentially increasing the odds of implantation and a successful pregnancy.
How the Laser Assisted Hatching Procedure Works
Let’s break down the steps of LAH as it fits into your IVF cycle:
Preparing the Embryo
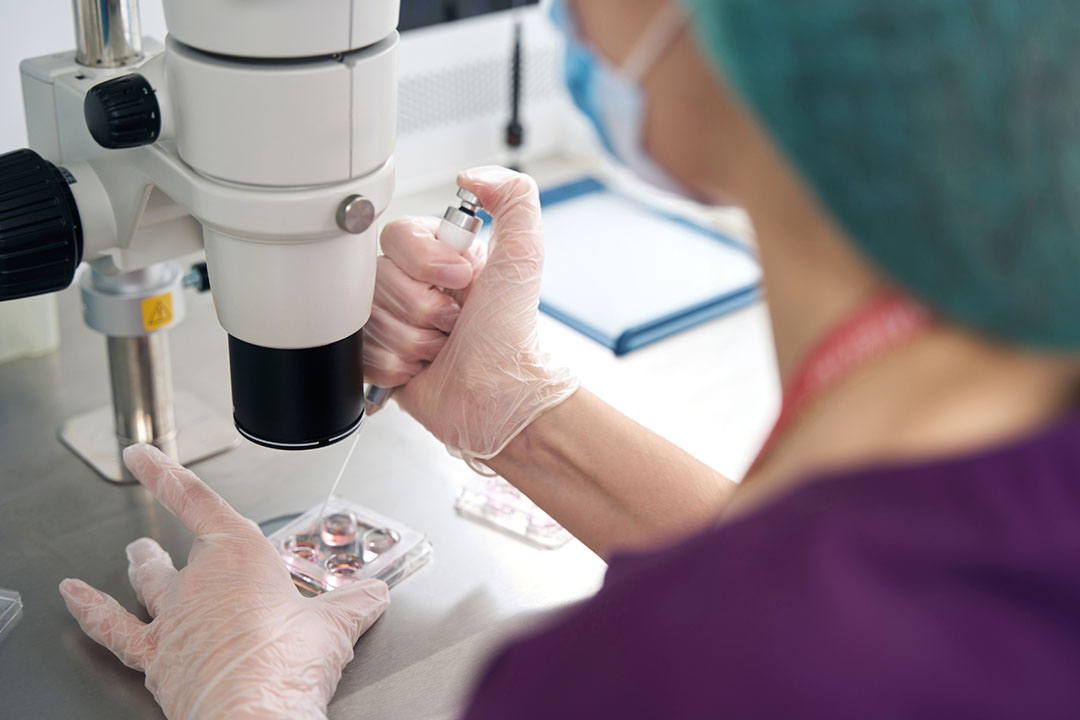
First, your embryo is gently removed from the incubator and placed in a special culture dish. This dish is then positioned under a micromanipulation microscope—a tool that allows the embryologist to get a close-up view of your embryo and its surrounding zona pellucida.
Applying the Laser
Once everything is set, the embryologist activates the laser system. With extreme care, the laser is directed at the targeted section of the zona pellucida. The laser’s energy is delivered in a few short bursts that serve either to thin the outer shell or to create a small hole in it. This process is highly controlled to ensure that only the zona pellucida is affected while leaving the embryo’s inner cells untouched.
Finishing Up
After the laser pulses have been applied, the embryo is returned to its culture dish and placed back in the incubator. It continues to develop normally until it’s ready to be transferred into the uterus. The entire LAH procedure is over in a matter of seconds, and when executed correctly, it poses no harm to the embryo.
Who Can Benefit from Laser Assisted Hatching?
LAH isn’t a standard procedure for every IVF cycle—it’s usually reserved for cases where there might be additional challenges. Here are some situations in which your fertility specialist might recommend LAH:
Multiple IVF Failures
If you have undergone two or more IVF cycles without a successful pregnancy, your doctor might consider LAH as a way to improve embryo implantation rates.
Frozen Embryo Transfers
Embryos that have been cryopreserved (frozen) sometimes develop a thicker zona pellucida during the freezing and thawing processes. LAH can help by weakening this barrier, which might otherwise hinder the embryo’s ability to hatch.
Advanced Maternal Age
Women aged 38 or older often experience a tougher zona pellucida in their embryos. In these cases, LAH may give the embryo a better chance of breaking free and implanting in the uterine lining.
Unexplained Fertility Issues
When all the usual tests come back normal yet pregnancy remains elusive, LAH might be offered as an additional technique to try and overcome subtle barriers to successful implantation.
Benefits of Laser Assisted Hatching
Research has shown that, in carefully selected groups, laser assisted hatching can enhance the likelihood of pregnancy. Here are some key benefits that many patients experience:
- LAH facilitates the embryo’s hatching process. This step is crucial because a successful hatching increases the chances that the embryo will attach properly to the uterine wall.
- For couples facing repeated IVF failures or for women with advanced maternal age or frozen embryos, LAH can be a beneficial complement to standard IVF techniques.
- One of the great advantages of LAH is that it is a very brief and non-invasive procedure. It takes only a few seconds and, when performed by experienced professionals, does not adversely affect the development of the embryo.
Potential Risks Associated with Laser Assisted Hatching
Like any medical procedure, LAH comes with a few risks. However, these risks are generally low, especially when the procedure is performed by experienced embryologists. Some potential risks include:
- There is a small risk that the laser might inadvertently damage the embryo if not used properly. Modern equipment and skilled technicians have minimized this risk significantly.
- In some cases, even after the application of LAH, the embryo might still struggle to hatch properly. This could potentially affect overall implantation and pregnancy outcomes.
- Although the risk is slight, there is some evidence suggesting that assisted hatching might be associated with an increased chance of multiple pregnancies, such as identical twins.
How LAH Fits into the IVF Process
Laser assisted hatching is typically integrated into an IVF cycle shortly before the embryo transfer. The timing can vary depending on whether you are undergoing a fresh or frozen cycle:
In fresh IVF cycles, LAH is usually performed on day three of embryo development. This timing helps to prepare the embryo for transfer while maintaining its overall integrity.
For embryos that have been cryopreserved, LAH is conducted after they have been thawed. Because frozen embryos can sometimes have a thicker or hardened zona pellucida as a side effect of the cryopreservation process, performing LAH after thawing is critical to help the embryo hatch once it is transferred into the uterus.
Once the procedure is complete, the embryo is returned to its culture medium and allowed to develop further before being transferred into your uterus.
The Technology Behind Laser Assisted Hatching
The success of LAH is largely due to modern laser technology. Here’s a glimpse into how it works behind the scenes:
- High-Precision Laser Systems: The laser used in LAH emits very short pulses of light, which are precisely controlled. These pulses are designed to affect only the zona pellucida without exposing the inner cells of the embryo to excessive heat or light.
- Advanced Micromanipulation Equipment: The procedure is performed under a microscope that provides a magnified view of the embryo, allowing the embryologist to target the exact spot for treatment.
- Controlled Energy Delivery: The laser’s energy is delivered in a manner that allows for either the thinning of the zona pellucida or the creation of a small opening. This precision ensures that the embryo’s delicate inner structures remain safe and intact.
Conclusion
Laser assisted hatching represents a promising and innovative tool in modern IVF treatment. By carefully creating a small opening or thinning the zona pellucida, LAH helps the embryo “hatch” and successfully implant into the uterine lining.
For patients facing challenges such as a thicker or hardened zona pellucida—whether due to natural factors, the effects of cryopreservation, or advanced maternal age—this procedure can be particularly beneficial.
The process itself is quick and minimally invasive, relying on the precision of modern laser technology and the expertise of skilled embryologists. While there are potential risks, these risks are generally low when the procedure is carried out by experienced professionals.
As clinical studies have shown, the use of LAH in selected patient groups has been associated with improved implantation and pregnancy rates.
About Us
AKsigen IVF is a premier center for advanced fertility treatments, with renowned fertility experts on our team. Specializing in IVF, ICSI, egg freezing, and other cutting-edge reproductive technologies, AKsigen IVF is committed to helping couples achieve their dream of parenthood. With personalized care and a patient-first approach, AKsigen IVF provides comprehensive fertility solutions under one roof.